How old is the universe?
Do you know how old is the universe? Some people may know a little about how old is the universe and some might not. Those little people who know might have some doubts. This information was used by astronomers to determine the age of the universe i.e. how old is the universe? Age may only be a number, but when it comes to the age of the universe, it's a pretty important one.
As per research, the universe is approximately 13.8 billion years old. We know age is just a number but when we talk about the age of the universe, it becomes hard to guess. As per the research till now, the universe is 13.8 billion years old in approximate. But how come the scientists are able to determine the age of the universe? The universe must be older than the oldest thing that exists in the universe itself. By studying the oldest objects in the universe and measuring how fast the universe is expanding, we can guesstimate the age of the universe. Thus to measure the age of the universe, we should go for ancient stars in the universe.
As per research, the universe is approximately 13.8 billion years old. We know age is just a number but when we talk about the age of the universe, it becomes hard to guess. As per the research till now, the universe is 13.8 billion years old in approximate. But how come the scientists are able to determine the age of the universe? The universe must be older than the oldest thing that exists in the universe itself. By studying the oldest objects in the universe and measuring how fast the universe is expanding, we can guesstimate the age of the universe. Thus to measure the age of the universe, we should go for ancient stars in the universe.
Age limits
The universe is a huge bubble of space and time that is continuously expanding in volume. If we go far and far enough years back when everything was a compact mass of incomprehensible density, there comes a moment in time the universe began. That’s the moment which should be the birth date of the universe.
So how old is the Universe? How long has it been expanding for? How do we know the age of the universe?
Mass is the basis of a star’s life cycle. Greater the mass, faster is the burn rate of stars in space than the stars having the lesser mass. A 10 times more massive star than the sun will burn through in 20 million years, while a star having half the mass of the sun’s mass will burn more than 20 million years. The mass is also affecting the brightness i.e. luminosity of a star. Clearly, massive stars are brighter. [Related: The Brightest Stars: Luminosity & Magnitude]
The first stars known as Population III stars were great in mass but lived a very short life, contained only hydrogen and helium. After the fusion, they created the other elements which helped in building the next generation of stars i.e. other types of stars.
“The detection of dust in the early universe yields new data on when the first supernovae exploded and henceforth when the first hot stars showered the universe in light,” European Southern Observatory officials uttered in a statement.” Finding out the timing of this ‘cosmic dawn’ is the most sought after thing in modern astronomy.
The early stars are not the only object to put limits on the age of the universe. The thickset of stars called as globular clusters have much the same attributes. The oldest familiar globular clusters have stars of age between 11 and 14 billion years old. There comes a wide range in the precise measurement of the distances to the clusters that affect the estimates of brightness and henceforth the mass. If the cluster is farther than the measured distances, the stars in that clusters would be brighter and hence more massive that means they are younger than what the scientists have calculated.
Archaeologists use fossils to build up the history of the Earth. Likewise, astronomers use globular clusters to build up the history of the galaxy. About 150 globular clusters are known in the milky way galaxy, out of which each globular cluster is a tracer of the galactic halo and the formation of the Milky Way Galaxy. This uncertainty puts limits on the age of the universe. It must b at least 11 billion years old. It should be older but can’t be younger for sure.
How fast is the universe expanding?
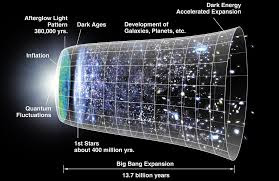 |
| How the universe is expanding |
Many factors determine the value of this constant. First of all, the type of matter that dominates the universe. Secondly, density is also a key to determine the Hubble constant. The low density of matter is older than a dense-matter.
Now how to determine density as well composition of the universe? We have to rely on missions by NASA’s Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) and The European Space Agency’s Planck spacecraft. The thermal radiation left after the Big Bang enables these missions to measure the density, composition and the rate of expansion of the universe. These radiations left after the Big Bang is known as the cosmic microwave background. The two missions have mapped it.
The age of the universe estimated by WMAP in 2012, is to be at least 13.77 billion years with 59 million years of uncertainty. Planck’s result measured the age of the universe at 13.82 billion years. The two measurements fall within the limit of 11 billion years. They had independently derived these numbers from the globular clusters with smaller uncertainties.
NASA used Spitzer Space Telescope to narrow down the age of the universe reducing the uncertainty of the Hubble constant. The combined results of NASA and WMAP measurements enabled the scientists to determine the size and age of the universe.

Comments
Post a Comment